Menu
Close
Close
- Shop
- Fruit & Vegetables
- Meat & Poultry
- Dairy & Eggs
- Nuts, Seeds, Legumes, & Flours
- Oils, Infusions, & Vinegars
- Pickles, Preserves, & Jams
- Salts, Seasonings, & Sauces
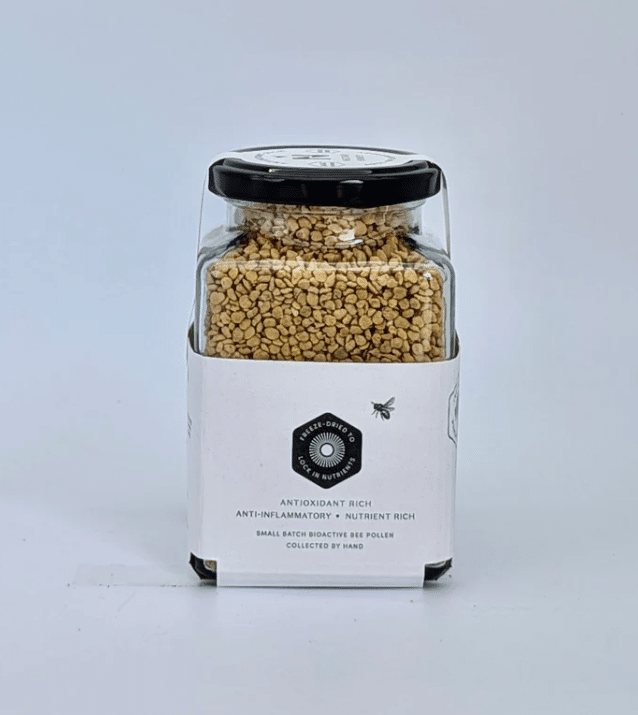
- Honey & Dried Fruit Snacks
- Sweet Treats
- Cold Drinks
- Hot Drinks
- Gardening, Composting, & Animal Feed
- Gifts & Homewares
- Health & Hygiene
- Meal Kits & Pre-Mixes
- Trees, Plants, & Seeds
- Farm Stays & Camping
- Wholesale
- Find a Producer
- Join the Network
- The Backyard Gazette
- Contact Us
- My account
- Cart
- Shop
- Fruit & Vegetables
- Meat & Poultry
- Dairy & Eggs
- Nuts, Seeds, Legumes, & Flours
- Oils, Infusions, & Vinegars
- Pickles, Preserves, & Jams
- Salts, Seasonings, & Sauces
- Honey & Dried Fruit Snacks
- Sweet Treats
- Cold Drinks
- Hot Drinks
- Gardening, Composting, & Animal Feed
- Gifts & Homewares
- Health & Hygiene
- Meal Kits & Pre-Mixes
- Trees, Plants, & Seeds
- Farm Stays & Camping
- Wholesale
- Find a Producer
- Join the Network
- The Backyard Gazette
- Contact Us
- My account
- Cart